
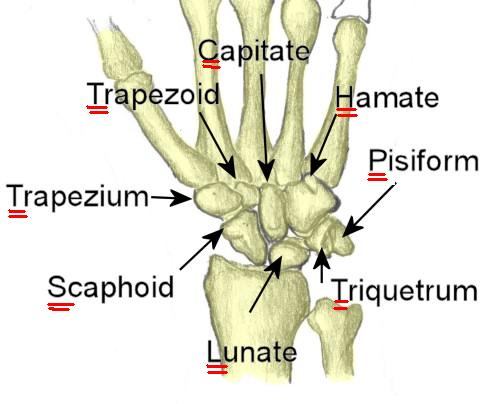
It can be slow to heal because of the limited circulation to the bone. The distal convex surface articulates with trapezium and trapezoid. The medial surface presents two articular facets of these, the superior or smaller is flattened of semilunar form, and articulates with the lunate bone the inferior or larger is concave, forming with the lunate a concavity for the head of the capitate bone. The lateral surface is rough and narrow, and gives attachment to the radial collateral ligament of the wrist. The volar surface is concave above, and elevated at its lower and lateral part into a rounded projection, the tubercle, which is directed forward and gives attachment to the transverse carpal ligament and sometimes origin to a few fibers of the Abductor pollicis brevis. On the dorsal surface is a narrow, rough groove, which runs the entire length of the bone, and serves for the attachment of ligaments. The inferior surface, directed downward, lateralward, and backward, is also smooth, convex, and triangular, and is divided by a slight ridge into two parts, the lateral articulating with the greater multangular, the medial with the lesser multangular. The superior surface is convex, smooth, of triangular shape, and articulates with the lower end of the radius.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
